-
Technology Governance Policy Research Unit
RCModel, a Risk Chain Model for Risk Reduction in AI Services
Technology Governance Policy Research Unit
With the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) services and products in recent years, issues related to their trustworthiness have emerged and AI service providers need to be prepared for various risks. The AI Governance Project of the Technology Governance Policy Research Unit, Institute for Future Initiatives, the University of Tokyo has been studying a framework for risk assessment and control of AI services. This recommendation is one of the outputs of the research.
In this policy recommendation, we propose a risk chain model (RCModel) that supports AI service providers in proper risk assessment and control. We hope that RCModel will contribute to the realization of trustworthy AI services. In the future, we plan to systematize the framework through joint research with various stakeholders.
Policy Recommendation
The full text can be downloaded below.
Abstract of the policy recommendation
Authors:
Takashi Matsumoto (Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu LLC/The University of Tokyo)
Arisa Ema (The University of Tokyo/RIKEN AIP Center)
Executive summary:
With the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) services and products in recent years, issues related to their trustworthiness have emerged and AI service providers need to be prepared for various risks. In this policy recommendation, we propose a risk chain model (RCModel) that supports AI service providers in proper risk assessment and control. We hope that RCModel will contribute to the realization of trustworthy AI services.
Overview of RCModel
1)Organization and structure of risk components
There are a number of potential risk factors involved in provision of AI services. In RCModel, these factors are segregated into (1) technical components of the AI system, (2) components related to the code of conduct (including communication with users) of the service provider, and (3) components related to the user’s understanding, behavior, and usage environment.
2)Identification of risk scenarios and risk-contributing factors
RCModel helps identify risk scenarios related to AI services, such as unfair decisions and uncontrollable accidents. It then identifies risk factors for priority risk scenarios.
3)Visualization of risk chains and planning risk control
Because it is difficult to reduce risk sufficiently on a factor basis, AI service providers can consider stepwise risk reduction by visualizing the relationships (risk chain) among the risk factors related to risk scenarios. This allows consideration of where a risk exists and its effective and efficient control.
Policy Recommendations for Future Development and Implementation of AI Services Using RCModel
Policy Recommendation 1: Enhance understanding of risk scenarios and factors
Service providers need to properly understand the risk factors associated with their AI services. They should also pay attention to social incidents involving the use of AI technologies and recognize important risk scenarios.
Policy Recommendation 2:Promotion of appropriate risk controls using RCModel
AI service providers should formulate their risk control measures by analyzing RCModel’s risk chain. It is neither necessary nor always possible to reduce all the risks identified; therefore, appropriate controls should be established within an enterprise based on factors such as magnitude of risks posed, technical difficulty, cost-effectiveness, and continuity.
Policy Recommendation 3:Promoting and updating dialogue among stakeholders
RCModel should be used to facilitate dialogue among AI service providers, AI developers, and users. In addition, a system should be established to clarify risk tolerance, create risk scenarios, structure risk factors, examine risk control models, and create a common understanding on the scope of each stakeholder’s responsibility.
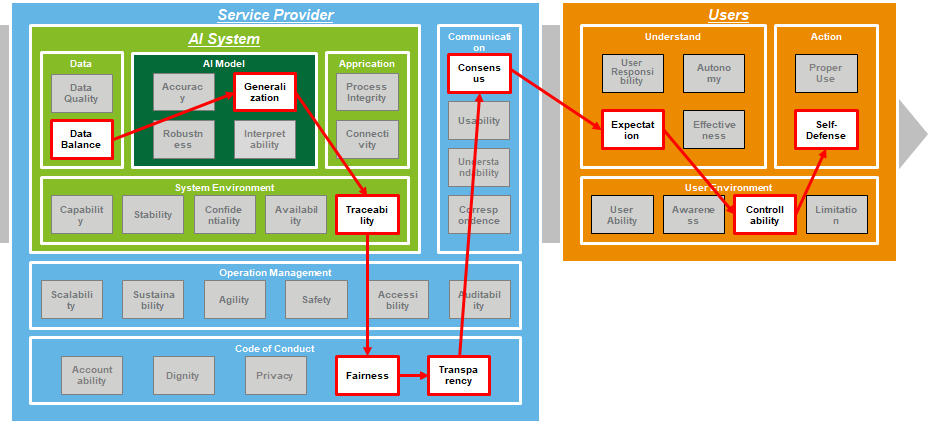
Example of risk factors and risk chain
This policy recommendation is based on the following draft paper:
akashi Matsumoto and Arisa Ema, “Proposal of the Model Identifying Risk Controls for AI Services,” The 34th Annual Conference of the Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence, 2020, Kumamoto, Japan, June 12, 2020,
https://confit.atlas.jp/guide/event/jsai2020/subject/4N2-OS-26a-02/tables?cryptoId=
This policy recommendation is published under the Creative Commons license CC-BY 4.0.